- 3 replies
- 2,094 views
- Add Reply
- 0 replies
- 1,264 views
- Add Reply
- 0 replies
- 1,178 views
- Add Reply
- 0 replies
- 1,627 views
- Add Reply
- 0 replies
- 897 views
- Add Reply
REVIEW: UAV IMAGE PROCESSING SOFTWARE

By Arhanghelul,
Here is an interesting review:
http://www.50northspatial.org/uav-image-processing-software-photogrammetry/
😉😊
Topcon showcases Products at Xponential 2019

By Lurker,
Topcon Positioning Group’s Dave Henderson offers a rundown on the company’s latest products, including the Falcon 8+ drone, Sirius Pro, MR-2 modular receiver, and B210 and B125 receiver boards, at Xponential 2019.
source:
https://www.gpsworld.com/topcon-showcases-falcon-8-drone-sirius-pro-and-receiver-boards-at-xponential-2019/
DT Research announced the DT301X-TR Rugged Tablet for Real time measurements

By Lurker,


DT Research, the leading designer and manufacturer of purpose-built computing solutions for vertical markets, today announced the DT301X-TR Rugged Tablet, a lightweight military-grade tablet that is purpose-built to enhance the precision for bridge and construction inspections, 3D surveying, mapping of underground utilities, and crime and crash scene reconstruction.
With 10.1” high-brightness capacitive touch screen that can easily be read in a wide range of lighting indoors and outdoors, a
New site from NASA, SpaceforUS, shows how its Earth data aids 50 states of America

By Lurker,
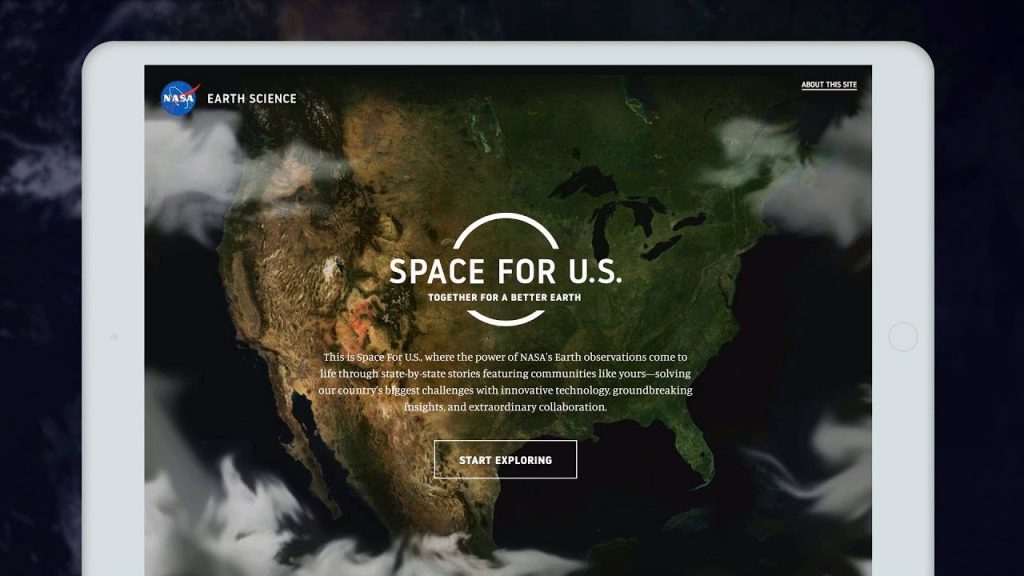

The state of Alaska is beautiful and wild — no wonder it is called the “Last Frontier”. The land has more than 130 volcanoes that pose a grave threat to the residents. A joint project by National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) has given scientists and forecasters a platform to protect people from volcanic ash.
This is one of the many case studies highlighted by the space agency on its new website, SpaceforUS, which inte
Tallysman release lightweight helical GNSS and iridium antennas

By Lurker,


Tallysman, a leading manufacturer of high performance GNSS and Iridium antennas, is announcing the first three products of a new range of helical antennas to be introduced in 2019.
The first three models of the Tallysman helical family are:
HC871 (25g) – A housed, dual band, active GNSS antenna, supporting GPS L1/L2, GLONASS G1/G2, Galileo E1, and BeiDou B1.
HC872 (36g) – A housed, dual band, active GNSS antenna, supporting GPS L1/L2, GLONASS G1/G2, Galileo E1, BeiDou B1, and
-
Forum Statistics
8.8k
Total Topics43.5k
Total Posts


